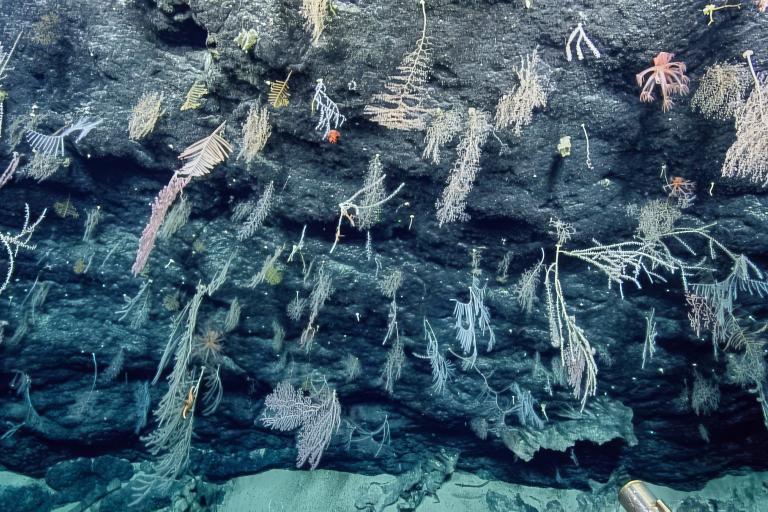
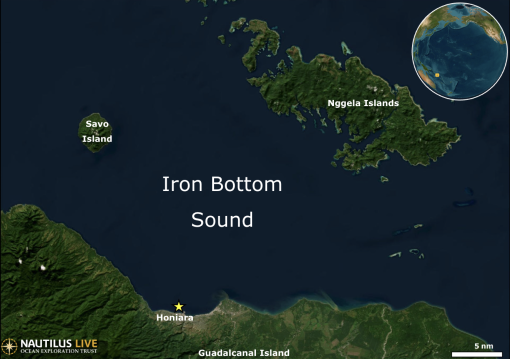
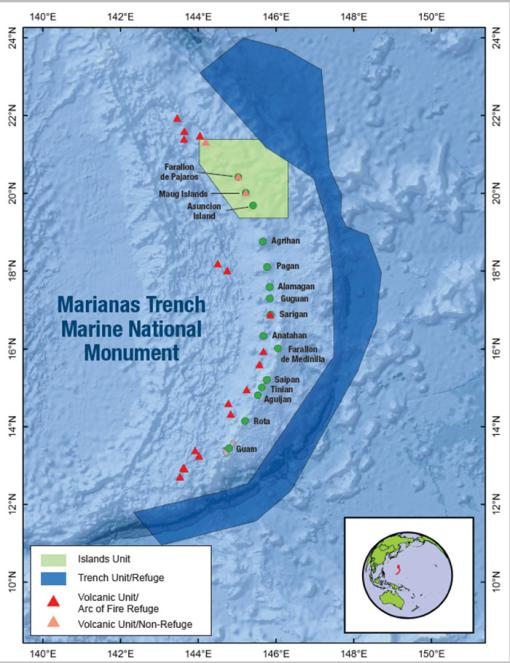
Update: Ongoing mechanical repair of a ship system has changed operational plans for the NA172 expedition, postponing the water column exploration and remotely operated vehicles portion of this expedition within the Mariana Trench Marine National Monument. The remainder of the expedition time will be dedicated to resolving these issues and mapping operations to acquire high-resolution bathymetry in areas where no data exists, through US waters around the Mariana Islands, in the Federated States of Micronesia, international waters, and the Solomon Islands. Seafloor mapping in unexplored areas directly contributes to the US National Strategy for Ocean Mapping, Exploration, and Characterization, the Beyond the Blue: Illuminating the Pacific campaign, and other coordinated initiatives.
The expedition will also include deployment of Argo floats to support ocean monitoring efforts by Scripps Institution of Oceanography to add important Western Pacific coverage to the over 3,800 floats that are currently operational in the global ocean. Additionally, operations will include topside surveys by trained seabird observers to assess the diversity and abundance of seabirds offshore.
This expedition is funded by NOAA Ocean Exploration via the Ocean Exploration Cooperative Institute.